The Enduring Legacy of Sheepdogs: Guardians of the Flock and Loyal Companions
For centuries, the pastoral landscapes of the world have echoed with the rhythmic bark of sheepdogs, guiding and guarding flocks across vast terrains. These intelligent, agile, and devoted canines, collectively known as sheepdogs or herding dogs, are more than just farmhands; they are integral partners to shepherds, guardians of livestock, and cherished companions. The term “sheepdog” encompasses a diverse group of breeds, each with unique characteristics and working styles, yet united by a shared ancestry and an innate herding instinct. This article will delve into the fascinating world of sheepdogs, exploring their history, diverse breeds, working abilities, and enduring legacy in both pastoral and domestic life.
A History Rooted in Pastoralism:

The history of sheepdogs is inextricably linked to the domestication of sheep and the rise of pastoralism. As humans transitioned from nomadic hunter-gatherers to settled agricultural societies, sheep became a vital source of food, wool, and trade. Managing these flocks across often expansive and challenging landscapes required a dedicated and intelligent partner, and thus, the sheepdog emerged.
Early sheepdogs were likely landrace breeds, evolving naturally in response to the specific demands of their environment and the herding tasks required. These early dogs were selected for traits such as intelligence, trainability, stamina, agility, and a strong herding instinct. Over time, as different regions developed unique sheep breeds and herding practices, distinct sheepdog breeds began to emerge, each adapted to their specific geographical location and working conditions.
A Tapestry of Breeds: Diversity in Herding Styles and Appearance
The world of sheepdogs is remarkably diverse, encompassing a wide array of breeds, each with its own unique history, physical characteristics, and herding style. While it’s impossible to cover every breed in detail, some of the most well-known and influential sheepdog breeds include:
-
Border Collie: Often hailed as the quintessential sheepdog, the Border Collie is renowned for its exceptional intelligence, intense focus, and unparalleled herding ability. Originating from the border region between Scotland and England, Border Collies are known for their “eye,” an intense gaze used to control sheep, and their agile, athletic movements. They are “gathering” dogs, excelling at rounding up sheep from a distance and bringing them to the shepherd. Their trainability and work ethic make them popular in herding competitions and various canine sports.
-
Australian Shepherd: Despite its name, the Australian Shepherd originated in the western United States, not Australia. Developed in the 19th century to herd livestock for Basque shepherds, Australian Shepherds are known for their versatility, intelligence, and striking appearance, often featuring merle coats and heterochromia (different colored eyes). They are energetic and trainable, excelling in both herding and as family companions for active households. They are considered “driving” dogs, adept at moving flocks forward and pushing them into confined spaces.
-
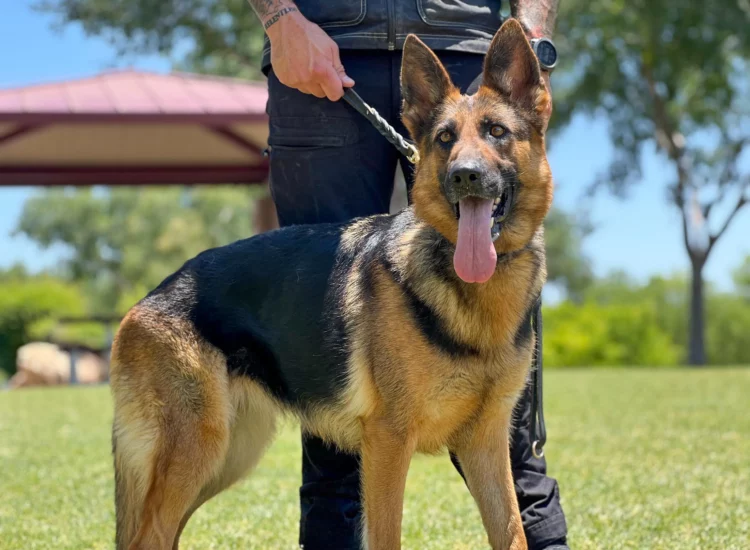
German Shepherd: While often recognized for their roles in police and military work, the German Shepherd Dog was originally developed in Germany as a herding dog. Their intelligence, trainability, and protective instincts made them ideal for managing large flocks and guarding them from predators. German Shepherds are versatile working dogs, capable of both gathering and driving, and their loyalty and trainability have made them popular family pets as well.
-
Shetland Sheepdog (Sheltie): Resembling a miniature Collie, the Shetland Sheepdog hails from the Shetland Islands of Scotland. Bred to herd Shetland sheep, which are smaller than mainland breeds, Shelties are intelligent, agile, and vocal herders. They are known for their alertness, trainability, and devotion to their families, making them excellent watchdogs and companions.
-
Old English Sheepdog: Instantly recognizable for their shaggy coats and bobbed tails, Old English Sheepdogs are an ancient breed with roots in southwestern England. Despite their fluffy appearance, they are strong and capable herders, traditionally used to drive cattle and sheep to market. They are known for their gentle nature, intelligence, and distinctive “bobtail bark.”
-
Welsh Corgi (Pembroke and Cardigan): Uniquely short-legged herders, Welsh Corgis, both Pembroke and Cardigan varieties, originated in Wales. Their low stature allowed them to nip at the heels of cattle and sheep, effectively driving them without being kicked. Corgis are intelligent, courageous, and surprisingly agile herders, known for their independent spirit and playful personalities.
-
Belgian Sheepdogs (Malinois, Tervuren, Groenendael, Laekenois): Representing four distinct varieties, Belgian Sheepdogs are intelligent, versatile, and highly trainable working dogs originating from Belgium. While differing in coat type and color, they share similar herding instincts, athleticism, and protective natures. Belgian Malinois, in particular, are widely used in police and military work due to their exceptional trainability and drive.
Working Abilities: Instinct, Training, and Partnership

Related articles 01:
1. https://chosloughi.org/the-enduring-charm-of-the-collie-a-breed-profile
2. https://chosloughi.org/the-most-child-friendly-dog-breeds-a-guide-for-families
3. https://chosloughi.org/a-celebration-of-canine-beauty-exploring-the-worlds-most-stunning-dog-breeds
4. https://chosloughi.org/the-sloughi-tracing-the-footsteps-of-a-north-african-treasure
5. https://chosloughi.org/five-compelling-reasons-to-welcome-a-shiba-inu-into-your-life
The remarkable herding abilities of sheepdogs are a combination of innate instinct, careful training, and a deep partnership with their shepherd. Herding instinct is deeply ingrained in these breeds, a complex set of behaviors driven by genetics and honed over generations. This instinct manifests in various ways, including:
- Gathering: The ability to round up scattered sheep and bring them together into a cohesive flock.
- Driving: Moving the flock forward in a desired direction, often across long distances.
- Flanking: Moving around the sides of the flock to prevent straying and maintain control.
- Holding: Keeping the flock in a specific location, preventing them from moving prematurely.
- Fetching: Going out to retrieve stray sheep and bring them back to the flock.
- Guarding: Protecting the flock from predators and other threats.
While instinct provides the foundation, training is crucial to refine and channel these natural abilities into effective herding work. Shepherds utilize various training methods, often starting with basic obedience commands and gradually introducing herding tasks. Training typically involves positive reinforcement, clear communication, and repetition, building a strong bond and understanding between dog and shepherd.
The partnership between shepherd and sheepdog is a remarkable example of interspecies cooperation. The shepherd provides direction and strategy, while the sheepdog executes the herding tasks with agility, intelligence, and tireless dedication. This partnership allows for efficient management of large flocks across vast and challenging terrains, a feat that would be nearly impossible for humans alone.
Beyond the Pasture: Sheepdogs as Companions and Competitors
While their primary purpose has historically been herding, sheepdogs have also proven to be exceptional companions and competitors in various canine sports and activities. Their intelligence, trainability, and energy make them well-suited for dog sports such as:
- Herding Trials: Competitive events that showcase the herding abilities of sheepdogs, judged on their skill, control, and partnership with the shepherd.
- Agility: Fast-paced obstacle courses that test a dog’s speed, agility, and responsiveness to commands.
- Obedience: Competitions that evaluate a dog’s ability to perform a series of commands accurately and reliably.
- Flyball: A relay race for dogs, combining speed, jumping, and retrieving skills.
- Disc Dog (Frisbee): A sport that showcases a dog’s athleticism and catching ability with flying discs.
Beyond competitive arenas, sheepdogs make wonderful family pets for active households willing to provide them with sufficient physical and mental stimulation. Their loyalty, intelligence, and trainability make them highly adaptable to family life, thriving on companionship and having a “job” to do, whether it’s herding children in the backyard or participating in daily walks and activities. However, prospective sheepdog owners must be aware of their high energy levels and need for consistent training and exercise to prevent boredom and potential behavioral issues.
An Enduring Legacy:
Sheepdogs represent a remarkable testament to the enduring partnership between humans and canines. From their humble origins as landrace herders to the diverse and refined breeds we know today, sheepdogs have played a vital role in pastoral societies for centuries. Their intelligence, loyalty, and tireless work ethic have not only shaped agricultural practices but have also earned them a place in our hearts as devoted companions and exceptional athletes. Whether guiding flocks across vast landscapes or excelling in canine sports, the legacy of sheepdogs continues to endure, a testament to their remarkable abilities and the enduring bond they share with humanity.
These resources offer in-depth information for those seeking to learn more about specific sheepdog breeds or the history and practice of sheep herding. Chắc chắn rồi, đây là bài viết dài 1200 từ về giống chó chăn cừu:
The Wonderful World of Sheepdog Breeds: A Comprehensive Guide

For centuries, humans have relied on the incredible partnership between themselves and dogs to manage livestock. Among these canine collaborators, sheepdogs stand out as intelligent, agile, and dedicated workers. These breeds, developed over generations, possess an innate herding instinct and a remarkable ability to control and guide flocks of sheep across vast landscapes. This article delves into the fascinating world of sheepdog breeds, exploring their history, characteristics, working styles, and the unique qualities that make them indispensable partners to shepherds and beloved companions to families worldwide.
The History and Purpose of Sheepdogs
The history of sheepdogs is deeply intertwined with the domestication of sheep and the development of agriculture. As humans transitioned from nomadic hunter-gatherers to settled agricultural societies, the need for efficient livestock management arose. Dogs, with their natural predatory instincts and trainability, proved to be invaluable allies in this endeavor.
Early sheepdogs were likely landrace breeds, evolving naturally in response to the demands of herding in specific geographic regions. Over time, humans selectively bred these dogs, emphasizing traits that enhanced their herding abilities, such as intelligence, stamina, agility, and a strong work ethic. This selective breeding led to the development of distinct sheepdog breeds, each adapted to the terrain, climate, and herding styles of their region of origin.
The primary purpose of sheepdogs is to assist shepherds in managing and moving flocks of sheep. Their responsibilities can include:
- Gathering: Bringing scattered sheep together into a cohesive flock.
- Driving: Moving flocks from one location to another, often over long distances.
- Penning: Guiding sheep into enclosures or pens.
- Sorting: Separating individual sheep or groups of sheep from the main flock.
- Protecting: Guarding flocks from predators.
Sheepdogs are not simply driven by instinct; they are highly trainable and responsive to commands. Shepherds rely on a combination of verbal cues, whistles, and hand signals to direct their dogs, creating a seamless and efficient partnership.
Related articles 02:
1. https://chosloughi.org/a-celebration-of-canine-beauty-exploring-the-worlds-most-stunning-dog-breeds
2. https://chosloughi.org/the-sloughi-and-its-hybrid-vigor-exploring-sloughi-mixes
3. https://chosloughi.org/five-compelling-reasons-to-welcome-a-chihuahua-into-your-life
4. https://chosloughi.org/four-paw-some-reasons-to-welcome-a-yorkshire-terrier-into-your-life
5. https://chosloughi.org/five-compelling-reasons-to-welcome-a-canine-companion-into-your-life
Key Characteristics of Sheepdog Breeds
While sheepdog breeds exhibit diversity in appearance and specific working styles, they share several key characteristics that make them well-suited for herding:
- Intelligence: Sheepdogs are renowned for their exceptional intelligence. They are quick learners, capable of understanding complex commands and adapting to changing situations in the field. This intelligence is crucial for making independent decisions while herding and responding effectively to the shepherd’s instructions.
- Herding Instinct: A strong herding instinct is the defining trait of sheepdogs. This instinct is innate, meaning it is genetically ingrained rather than learned. It manifests as a desire to control movement, often seen in behaviors like circling, nipping at heels, and using body language to direct animals.
- Stamina and Energy: Herding work is physically demanding, often requiring dogs to work for hours in challenging terrain and weather conditions. Sheepdogs possess remarkable stamina and energy levels, enabling them to maintain focus and effectiveness throughout long workdays.
- Agility and Speed: Agility and speed are essential for navigating flocks of sheep and responding quickly to their movements. Sheepdogs are typically athletic and nimble, capable of running, turning, and maneuvering effectively in open fields and rugged landscapes.
- Trainability and Responsiveness: Sheepdogs are highly trainable and eager to please their handlers. They thrive on working in partnership with humans and are responsive to commands, making them ideal for herding tasks that require close collaboration with the shepherd.
- Loyalty and Dedication: Sheepdogs develop strong bonds with their shepherds and are fiercely loyal and dedicated to their work. They are often described as having a strong work ethic and a deep desire to please their handlers, making them reliable and devoted partners.
Popular Sheepdog Breeds: A Closer Look

The world of sheepdog breeds is diverse, with each breed possessing unique characteristics and working styles. Here are some of the most popular and well-known sheepdog breeds:
-
Border Collie: Often hailed as the quintessential sheepdog, the Border Collie is renowned for its exceptional intelligence, intense work ethic, and “eye” – a hypnotic gaze used to control sheep. Originating from the border region between Scotland and England, Border Collies are highly energetic and require significant mental and physical stimulation. They excel in herding trials and are often considered the most intelligent dog breed. Their herding style is characterized by a crouching posture and intense focus, enabling them to control even the most challenging flocks.
-
Australian Shepherd: Despite its name, the Australian Shepherd originated in the western United States, not Australia. Developed to herd livestock in the American West, Australian Shepherds are intelligent, versatile, and energetic dogs. They are known for their striking appearance, often with merle coats and different colored eyes. Australian Shepherds are adaptable herders, capable of working various types of livestock in diverse terrains. They are also popular family pets, known for their loyalty and playful nature, but require ample exercise and mental stimulation.
-
German Shepherd: While often associated with police and military work, the German Shepherd Dog was originally developed in Germany as a herding dog. They are intelligent, trainable, and versatile, capable of both gathering and tending flocks. German Shepherds are known for their strength, courage, and protective instincts, making them effective guardians of livestock. Their herding style is more upright and assertive compared to the Border Collie. They are also highly adaptable and excel in various canine activities, including obedience, agility, and protection work.
-
Old English Sheepdog: Instantly recognizable for its shaggy coat and bobtail, the Old English Sheepdog is a gentle and good-natured breed that originated in England. Despite their fluffy appearance, they are strong and capable herders, traditionally used to drive cattle and sheep to market. Old English Sheepdogs are known for their “bear-like shuffle” gait and a distinctive “pot-casse” bark. While they can be effective herders, they are also popular family pets, known for their affectionate and playful personalities, especially with children.
-
Shetland Sheepdog (Sheltie): Resembling a miniature Collie, the Shetland Sheepdog hails from the Shetland Islands of Scotland. Shelties are intelligent, agile, and vocal herders, originally used to herd sheep and ponies in the rugged Shetland terrain. They are known for their alertness and barking, making them excellent watchdogs. Shelties are also popular companion dogs, known for their loyalty, trainability, and affectionate nature with families.
-
Welsh Corgis (Pembroke and Cardigan): These small but sturdy breeds from Wales are surprisingly effective herders, particularly of cattle and smaller livestock. Welsh Corgis, both Pembroke and Cardigan varieties, are intelligent, courageous, and low-set, allowing them to nip at the heels of livestock while avoiding kicks. They are known for their independent nature and strong will, but also their loyalty and affectionate personalities. Corgis have become increasingly popular as companion dogs, renowned for their charm and adaptability.
Beyond Herding: Sheepdogs as Companions and Working Partners
While their primary historical role is herding livestock, sheepdog breeds have proven to be remarkably versatile and adaptable, excelling in various roles beyond the farm. Their intelligence, trainability, and loyalty make them well-suited for:
- Companion Animals: Many sheepdog breeds, when provided with adequate exercise and mental stimulation, thrive as family pets. Their loyalty, affectionate nature, and protectiveness make them excellent companions, particularly for active families who can provide them with the attention and activity they need.
- Service Dogs: The intelligence and trainability of sheepdogs make them well-suited for service dog roles, assisting individuals with disabilities. They can be trained as guide dogs for the visually impaired, hearing dogs for the deaf, and mobility assistance dogs for those with physical limitations.
- Therapy Dogs: Sheepdogs’ gentle and empathetic nature makes them excellent therapy dogs, providing comfort and support to individuals in hospitals, nursing homes, and other care facilities.
- Search and Rescue Dogs: Certain sheepdog breeds, particularly German Shepherds and Border Collies, are utilized in search and rescue operations due to their intelligence, scenting abilities, and trainability.
- Police and Military Dogs: German Shepherds, in particular, are widely used as police and military dogs due to their strength, courage, trainability, and protective instincts.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Sheepdog Breeds
Sheepdog breeds represent a remarkable testament to the enduring partnership between humans and dogs. Bred for centuries to assist in livestock management, these intelligent, agile, and dedicated canines have played a vital role in agricultural societies worldwide. Beyond their herding prowess, sheepdogs have proven to be versatile and adaptable companions, excelling in various roles that showcase their intelligence, loyalty, and unwavering work ethic. Whether working tirelessly in the fields, providing assistance as service dogs, or enriching lives as beloved family pets, sheepdog breeds continue to captivate and inspire with their remarkable abilities and unwavering devotion. Their legacy as invaluable working partners and cherished companions is sure to endure for generations to come.