The Apex Hunters: Exploring the World of Predatory Dog Breeds
For millennia, dogs have stood by humanity’s side, evolving from wild canids into the diverse tapestry of breeds we know today. Within this incredible spectrum of canine forms and functions lies a distinct group: the predatory dog breeds. These are dogs sculpted by both natural selection and human design to excel in the art of the hunt. More than mere pets, they are living legacies of a time when canine skill was vital for survival and sustenance.
Understanding predatory dog breeds requires delving into the very essence of what it means to be a predator. It’s about more than just chasing and catching; it’s a complex interplay of instinct, physical prowess, and specialized senses honed over generations to locate, pursue, and subdue prey. These breeds aren’t simply dogs with a ‘prey drive’; they embody a suite of traits meticulously refined for specific hunting roles.
This exploration will take us into the captivating world of predatory dog breeds. We will examine different categories based on their hunting styles, spotlighting specific breeds within each, and uncover the remarkable adaptations that make them apex hunters in their own right.
Defining the Predatory Dog: Instincts and Adaptations
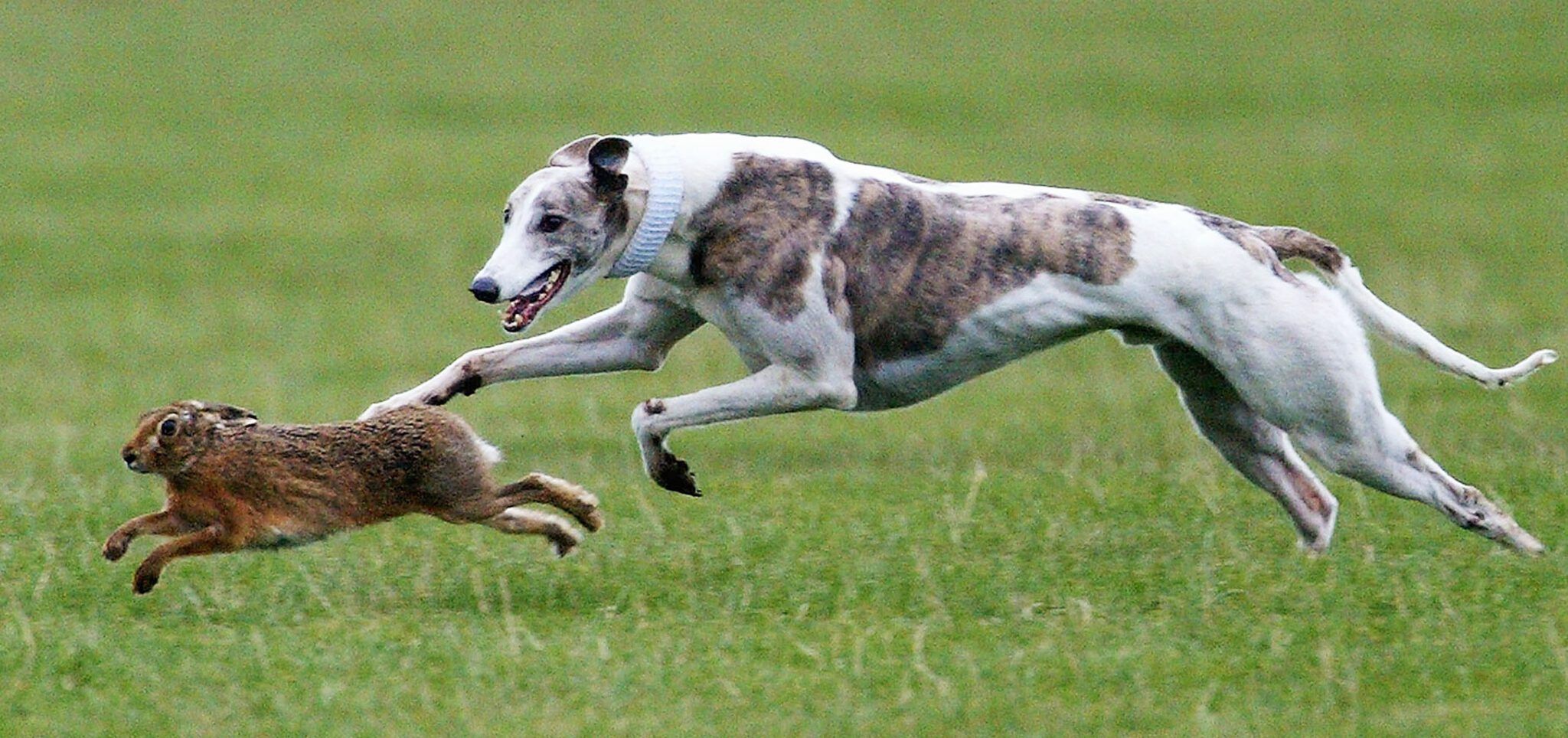

Predatory dogs stand apart due to their heightened predatory instincts. This isn’t simply about aggression – it’s about a focused, innate drive to seek, pursue, and capture. These instincts manifest in several key ways:
- Heightened Senses: Predatory breeds often possess exceptional senses tailored for hunting. Sighthounds have extraordinary vision for spotting prey at great distances. Scenthounds boast unparalleled olfactory capabilities, able to track faint trails across miles. Even terriers, bred to hunt vermin underground, have keen senses of smell and hearing to locate quarry in burrows.
- Physical Prowess: Speed, agility, stamina, and strength are hallmarks of predatory breeds. Sighthounds are built for explosive bursts of speed in open terrain. Scenthounds are endurance runners, capable of following scents for hours. Terriers are compact and agile, built for navigating tight spaces.
- Specialized Hunting Techniques: Different breeds employ diverse hunting strategies. Sighthounds rely on sight and speed to chase down fast prey. Scenthounds work methodically, using scent to track and flush out game. Terriers are tenacious diggers and fighters, designed to confront prey in their dens.
- Independent Thinking and Focus: Predatory hunting often requires dogs to work independently, making decisions in the field based on their instincts and training. They exhibit remarkable focus and determination once engaged in the hunt.
Categories of Predatory Dog Breeds: A Spectrum of Hunting Styles
To better understand the diverse world of predatory dog breeds, we can categorize them based on their primary hunting methods and prey types:
1. Sighthounds: The Speed Hunters
Sighthounds, or gazehounds, are the sprinters of the canine world. They hunt primarily by sight, relying on exceptional vision and incredible speed to chase down fast-moving prey in open landscapes. These breeds are characterized by:
- Exceptional Vision: Wide field of vision and keen eyesight allow them to spot prey from afar.
- Aerodynamic Build: Deep chests, slender bodies, long legs, and flexible spines are designed for explosive acceleration and top speeds.
- Chase and Capture Style: Sighthounds excel at pursuing fleet-footed game like hares, gazelle, and deer. They rely on bursts of speed to overtake prey and often dispatch it with a swift bite.
Examples of Sighthound Breeds:
- Greyhound: The epitome of canine speed, Greyhounds are capable of reaching speeds up to 45 mph. Originally used for coursing hare and deer, they are now renowned for racing and lure coursing.
- Saluki: One of the oldest dog breeds, Salukis were revered by ancient Egyptians and Persian nobility for their hunting prowess in pursuing gazelle and other desert game. They are known for their stamina and elegance.
- Afghan Hound: With its distinctive flowing coat, the Afghan Hound is built for hunting in mountainous terrains. They possess a combination of speed and agility, capable of navigating rough landscapes while pursuing prey like hares and foxes.
- Irish Wolfhound: The tallest of the sighthounds, Irish Wolfhounds were developed to hunt wolves and elk. Their imposing size and strength allowed them to confront large and formidable prey.
- Whippet: A smaller sighthound, the Whippet is often referred to as the “poor man’s racehorse.” They are incredibly fast and agile, excellent at coursing rabbits and hares.
- Borzoi (Russian Wolfhound): Bred by Russian aristocracy to hunt wolves in packs, Borzoi combine speed with surprising strength and a thick coat to withstand harsh climates.
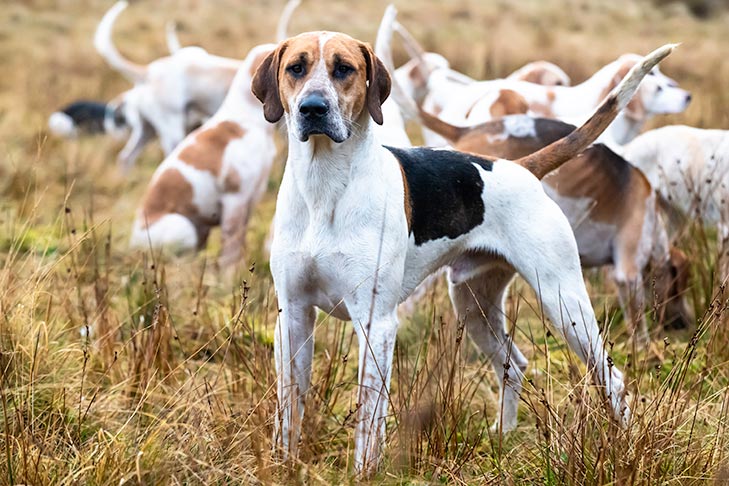
2. Scenthounds: The Trail Blazers
Scenthounds are masters of olfaction. Their world is one of scent, and they are driven by an insatiable urge to follow trails, using their noses to track game over vast distances. Key traits of scenthounds include:
- Exceptional Sense of Smell: Scenthounds have an extraordinary olfactory system, with millions more scent receptors than humans. Their long ears and loose skin help trap and funnel scents towards their noses.
- Stamina and Perseverance: Scenthounds are built for endurance, capable of following trails for hours, often in challenging terrain. They are methodical and persistent trackers.
- Pack Hunting Mentality: Many scenthounds traditionally hunt in packs, relying on cooperation and vocalizations to communicate and drive game.
Examples of Scenthound Breeds:
- Beagle: Perhaps the most recognizable scenthound, Beagles are cheerful and tireless rabbit hunters. Their compact size and keen noses make them ideal for navigating dense undergrowth.
- Bloodhound: With an unparalleled sense of smell, Bloodhounds are legendary trackers, able to follow even faint and aged scent trails. They are often used in law enforcement for search and rescue and tracking criminals.
- Basset Hound: Despite their short legs, Basset Hounds are determined and methodical trackers of rabbits and other small game. Their mournful baying is a distinctive feature of their hunting style.
- Coonhound (various breeds like Black and Tan, Bluetick, Redbone): Developed in America, Coonhounds are specialized in tracking raccoons and other tree-dwelling game. They are known for their loud, melodious bays that allow hunters to follow their progress through the woods.
- Foxhound (English Foxhound and American Foxhound): Bred for pack hunting of foxes, Foxhounds are tireless runners with a strong pack instinct. They are renowned for their stamina and vocalizations during the chase.
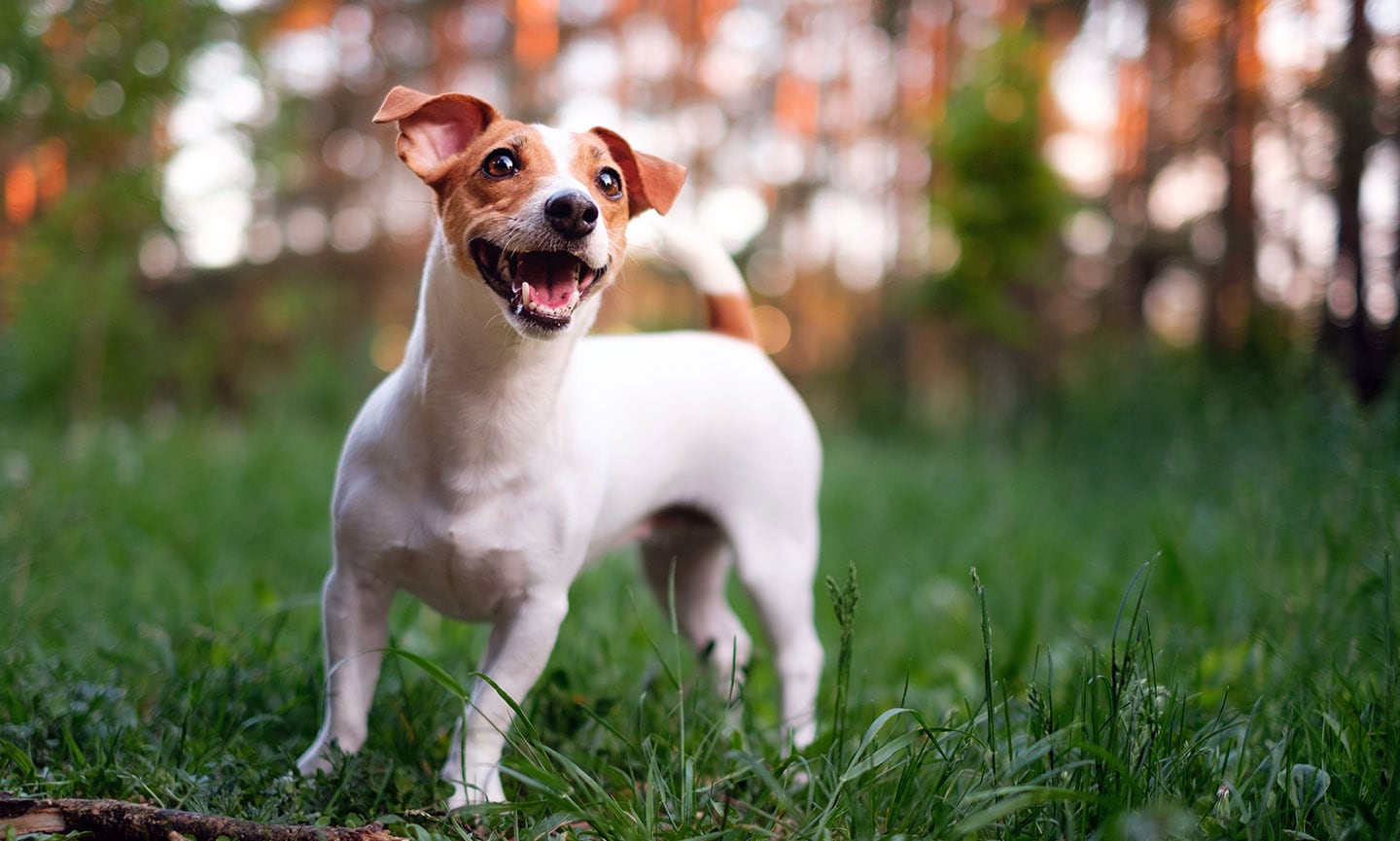
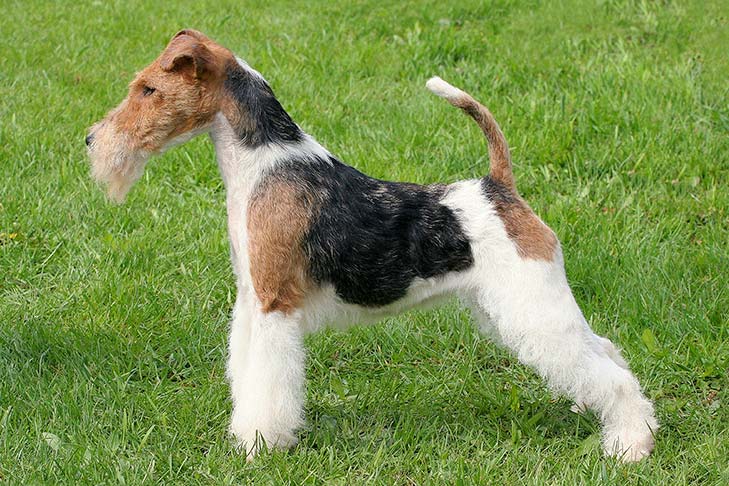
3. Terriers: The Earth Dogs and Vermin Hunters
Terriers, derived from the Latin “terra” for earth, are a group of breeds developed to hunt vermin and small game that live underground or in dens. They are characterized by:
- Small to Medium Size and Compact Build: Allows them to navigate tight spaces and burrows.
- Fearless and Tenacious Nature: Terriers are known for their boldness and determination in confronting prey, often much larger than themselves.
- Strong Digging Instincts: They are natural diggers, capable of excavating burrows to reach their quarry.
- Rough or Wiry Coats: Provide protection from undergrowth and harsh conditions in burrows.
Examples of Terrier Breeds:
Related articles 02:
1. https://chosloughi.org/a-celebration-of-canine-beauty-exploring-the-worlds-most-stunning-dog-breeds
2. https://chosloughi.org/the-ancient-mystery-the-importance-and-uniqueness-of-the-xoloitzcuintli
3. https://chosloughi.org/the-enduring-vigil-of-hachiko-a-true-story-of-unwavering-canine-devotion
4. https://chosloughi.org/the-sloughi-tracing-the-footsteps-of-a-north-african-treasure
5. https://chosloughi.org/top-guardian-dog-breeds-canine-protectors-for-home-and-family
- Jack Russell Terrier: Energetic and tenacious, Jack Russell Terriers were originally bred to hunt foxes and other vermin. Their small size and fearless nature make them excellent earth dogs.
- Fox Terrier (Wire Fox Terrier and Smooth Fox Terrier): Bred to bolt foxes from their dens during fox hunts, Fox Terriers are quick, agile, and persistent hunters.
- Border Terrier: Originating from the border region between England and Scotland, Border Terriers were used to hunt foxes and vermin in rocky terrain. They are known for their stamina and ruggedness.
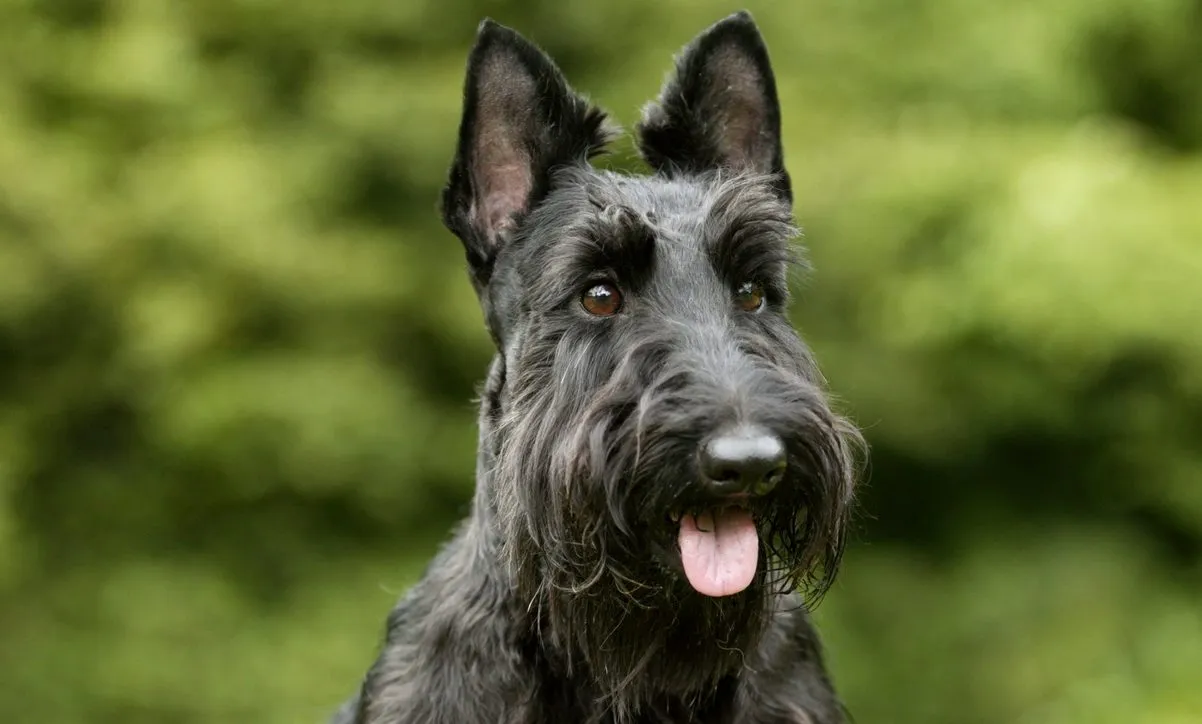
- Scottish Terrier: With their distinctive wiry coat and independent spirit, Scottish Terriers were developed to hunt badgers and other vermin in the Scottish Highlands.
4. Retrievers and Game Dogs: Multi-Purpose Hunters
While perhaps less “predatory” in the traditional sense of actively pursuing and dispatching wild prey independently, certain breeds, often categorized as gun dogs or sporting dogs, have strong predatory instincts honed for assisting human hunters. These include:
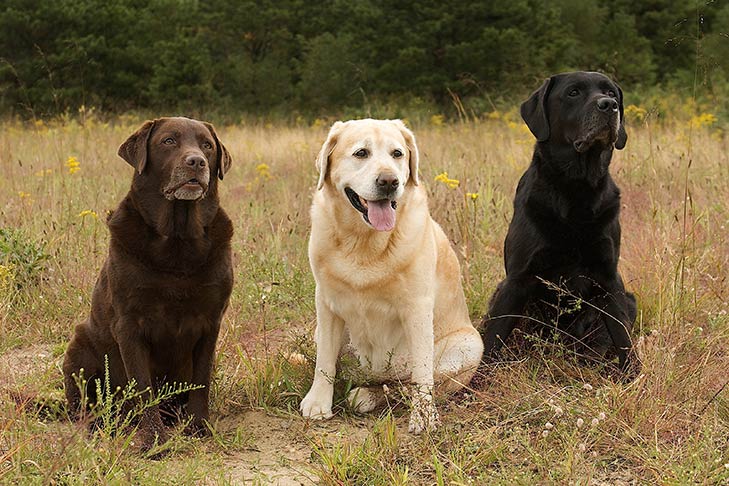
- Retrievers (Labrador Retriever, Golden Retriever, Chesapeake Bay Retriever): Bred to retrieve waterfowl and game birds that have been shot by hunters, retrievers exhibit a strong retrieving instinct which is a modified form of predatory behavior – bringing prey back to the pack (human hunter). They have soft mouths to avoid damaging game and a love for water.
- Pointers and Setters (German Shorthaired Pointer, English Setter): These breeds work closely with hunters to locate game birds. Pointers ‘point’ with their body, indicating the location of birds. Setters ‘set’ or crouch low, similarly indicating game. These breeds have a strong prey drive focused on birds and a cooperative nature with human hunters.
Living with Predatory Breeds: Responsibilities and Considerations
Owning a predatory dog breed is a unique and rewarding experience, but it comes with responsibilities. Their inherent instincts require understanding, management, and appropriate outlets.
- Exercise and Mental Stimulation: Predatory breeds need substantial exercise to channel their energy and prey drive constructively. This could include running, swimming, hiking, fetch, lure coursing, scent work, and other activities that mimic aspects of hunting.
- Training and Socialization: Early and consistent training is crucial for managing their instincts and ensuring they are well-behaved companions. Recall training is paramount, as is impulse control. Socialization with people and other animals is essential from a young age.
- Prey Drive Management: Owners need to be mindful of their dog’s prey drive, especially around smaller animals like cats, rabbits, or rodents. Safe management, secure fencing, and leash control are important to prevent unwanted chasing or harm.
- Understanding Breed-Specific Needs: Each predatory breed has unique needs based on its historical purpose and instincts. Researching your breed’s specific traits will help you provide the most appropriate care and environment.
Conclusion: Appreciating the Legacy of the Hunt
Predatory dog breeds represent a fascinating chapter in the history of dogs and their partnership with humans. They are living embodiments of canine skill, instinct, and adaptation, shaped by centuries of hunting alongside humans. While many of these breeds are now beloved companions, understanding and respecting their predatory heritage is crucial for responsible ownership and for appreciating the remarkable diversity of the canine world. These apex hunters continue to captivate us with their athleticism, intelligence, and the enduring echo of their wild ancestry.

:strip_icc()/GettyImages-1273562658-78041f1f54494eb692b01e8c6ad2c187.jpg)










:strip_icc()/BorderTerrierGettyImages-531551140CaptureLight-25a9cfa1a0b94bb68ea1848f84fe181c.jpg)